Clear Advantages: Low-pressure Electrolytic Ozone Ensures Drinking Water Safety
Release date:
2024-09-23

- The Current Status of Modern Drinking Water Sources
The state of water pollution in our country is cause for serious concern, particularly with regard to modern water sources, which are contaminated to varying degrees by severe organic pollutants. According to studies conducted from 1975 to 1992 on drinking water, the number of chemical contaminants found in treated drinking water surged from over 300 to as many as 785. Both surface water and groundwater sources are polluted to differing extents. Moreover, some reports from the United States reveal an even more alarming situation. The article "Troubled Water on Tape" states: "Since 1974, over 2,100 contaminants have been identified in U.S. drinking water, of which 190 are known or suspected to pose harmful effects on human health when reaching certain concentrations. Among these, 97 are confirmed or suspected carcinogens, 82 are mutagens or suspected mutagens, 28 are acute and chronic toxic substances, and 23 are tumor-inducing agents. The remaining 90 percent of organic compounds have yet to be identified." Internationally, standards for drinking-water quality are becoming increasingly stringent. Our country is also revising its water-quality standards, making the assurance of drinking-water quality an issue of pressing concern for the public.
Our city’s rural areas are among those severely affected by water pollution. In recent years, due to inadequate industrial pollution control, contamination from pesticides and fertilizers, pollution from aquaculture on water surfaces, and pollution from domestic waste, the well water, pond water, stream water, and even tap water commonly used for daily drinking in rural areas have all been contaminated to varying degrees. In particular, the groundwater drawn from wells dug by farmers themselves—typically 30 to 60 meters deep—generally fails to meet water quality standards. According to surveys, as many as 56.1% of our city’s water monitoring sites have failed to meet the required standards, leaving approximately one million people across the city without access to safe, potable tap water. According to information provided by the city’s Center for Disease Control, the pathogens responsible for most cases of hepatitis, cancer, and intestinal diseases can be traced back to the consumption of unsafe drinking water. Improving water quality and safeguarding the health of our people has now become an urgent priority.
- Standards for Drinking Water Quality
To safeguard people’s physical health and prevent the spread of diseases, drinking water must meet high-quality standards and comply with relevant national regulations. The treatment of drinking water and other facilities must adhere to the nation’s hygiene management regulations. Both China’s Ministry of Health and Ministry of Construction have issued specific standards and requirements (GB 5749-85).
1 1. Colority not exceeding 15 degrees; 2. Turbidity not exceeding 3 degrees.
3 1. No unusual odors or tastes are allowed. 2. No visible foreign matter is permitted.
5 • The pH value is between 6.5 and 8.5. • The oxide content is no more than 250 mg/L.
7 1. Cyanide no greater than 1.0 mg/L; 8. Total hardness no greater than 450 mg/L
9 • Iron content not greater than 0.3 mg/L • Total dissolved solids not greater than 1000 mg/L
11 1. The total bacterial count shall not exceed 100 CFU/ml. 12. The total coliform count shall not exceed 3 CFU/L.
In addition to the sensory characteristics and general chemical indicators mentioned above, there are also stringent controls on toxicological and radiological indicators. To ensure that drinking water meets the national hygiene standards, it is essential to subject it to purification treatment, thereby safeguarding human health and conserving water resources.
- Analysis of Types and Effects of Disinfectants
- Types of Disinfectants
-
1 1. Liquid chlorine; 2. Sodium hypochlorite; 3. Chlorine dioxide; 4. Ultraviolet light; 5. Ozone; 6. Dichloroisocyanuric acid; 7. Trichloroisocyanuric acid; 8. Sodium trichloroisocyanurate
Practice has proven that these disinfectants are all effective, but their disinfection effects differ.
-
Chlorine dioxide is a relatively ideal disinfectant. As an oxidizing agent, it reacts with organic substances in water to form various oxidation products. Today, chlorine dioxide is widely used for the disinfection of drinking water and certain types of wastewater. It is more effective than chlorine-based agents in killing bacteria and viruses. However, its main drawbacks are as follows: First, chlorine dioxide is an extremely unstable compound that is highly sensitive to factors such as temperature, pressure, and light. It can explode upon contact with sparks, organic materials, or when its concentration exceeds 4%. Second, the primary products of chlorine dioxide contain a certain amount of free chlorine, which can generate chlorides during the disinfection process. Therefore, its concentration should not be too high when used. Moreover, after disinfection, the residual chlorine concentration in discharged wastewater must be strictly controlled; excessively high residual chlorine levels can have severely harmful effects on receiving water bodies. According to U.S. regulations, the total residual chlorine content in effluent discharged into the ocean must not exceed 0.002 mg/L over a six-month period, with a maximum instantaneous value of no more than 0.126 mg/L.
★ Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent and can be described as a broad-spectrum, highly effective disinfectant. Its application has a history of nearly a century; ozone was first used as a disinfectant for water treatment. From the 1950s to the 1960s abroad, countries including the United States, France, Canada, Germany, Japan, Poland, and Switzerland had already begun widely adopting ozone technology—from drinking water and tap water to swimming pool water, and expanding its use to aquaculture, pharmaceutical production, and industrial wastewater treatment, among other areas. Internationally, over a thousand large- and medium-sized municipal water treatment plants alone have adopted ozone disinfection for drinking water. When used for drinking water disinfection, ozone kills bacteria and viruses much faster than other disinfectants; its effectiveness in eliminating microorganisms is 600 to 3,000 times greater than that of chlorine. Water treated with ozone produces fewer harmful byproducts and can increase the dissolved oxygen content in the water. It also removes color and odors, inhibits and kills algae in water, and can oxidize or decompose iron, manganese, pigments, suspended particulates, organic pesticides, and detergents present in the water. As a result, water treated with ozone is colorless, odorless, and has an excellent taste, effectively improving the quality of drinking water. Therefore, in developed countries today, ozone is not only used for drinking water disinfection but is also extensively applied in purifying water for beverages, food processing, centralized air-conditioning cooling systems, swimming pools, and both freshwater and seawater aquaculture. In recent years, developing countries with rapidly growing economies have also begun to adopt ozone widely as a disinfectant. Based on the promising prospects for ozone applications, our company is dedicated to the research and development of ozone generators, and we have already achieved successful applications in a variety of industries.
4. Using ozone to treat drinking water
Ozone is used for disinfecting drinking water because it acts quickly, delivers reliable results, effectively removes color and odors, and can degrade harmful substances in the water while also eliminating heavy metal ions and various organic impurities. However, when using ozone for drinking water disinfection, the specific dosage of ozone should be determined through experimentation based on the quality of the water being treated. According to our company’s practical experience, for relatively clean water, the typical ozone concentration added is 0.4–1.0 mg/L; after a contact time of 5–10 minutes, the residual ozone concentration in the water should be maintained at 0.1–0.5 mg/L. For water with more severe contamination, the ozone dosage can be increased to 3–6 mg/L, which generally achieves the desired disinfection effect.
-
Ozone Dosage and Contact Reaction Time Reference Table
Processing requirements
Ozone dosage
(mg/L water)
Removal rate
(%)
Contact time
(min)
Sterilize and inactivate viruses
1 -3
90 -99
Depending on the type of contact device, the duration ranges from a few seconds to 10 minutes.
Deodorizing, odor removal
1 -2.5
80
71
Decolorization
2.5 -3.5
80 -90
75
Remove iron, remove manganese
0.5 -2
90
71
Cash on Delivery
1 -3
40
75
CN
2 -4
90
73
ABS
2 -3
95
71
Phenol
1 -3
95
71
-
Note: 1) The solubility of ozone in water is also affected by water temperature: ozone's solubility in water decreases as the temperature drops and increases as the pressure rises. The key lies in properly designing the ozone dosage and ensuring good gas-to-water mixing to meet the required standards.
2 For the specific concentrations and contact times required to effectively eliminate various bacteria and viruses in water using ozone, please refer to the test report from the Chinese Academy of Preventive Medicine.
- Main issues to note when using ozone for drinking water disinfection
- Ozone Generator Selection:
-
Priority should be given to selecting manufacturers that specialize in the production of ozone generators. Our company is a prime example of such a specialized manufacturer—possessing not only proven experience and products successfully applied in drinking water disinfection, but also offering corresponding technical support and after-sales services. Overall, its performance is more reliable.
- The outlet concentration of ozone generators—the economically viable concentration of ozonated gas produced by ozone generators currently manufactured in China—is 8 to 12 mg/L.
- When using ozone generators to treat drinking water, it is especially important to ensure that the ozone generator produces ozone with a high purity and low levels of nitrogen oxides and other nitrogen-containing compounds, thereby avoiding the formation of new contaminants such as nitrites during the drinking water treatment process.
-
2 . Selection of gas mixing equipment
The mixing of gases with water has always been a challenging issue, and this becomes even more critical when it comes to the mixing of ozone gas with water. If the mixing efficiency is low, a large number of bubbles will rise to the water surface, not only wasting significant amounts of ozone gas but also causing environmental pollution to varying degrees as these ozone bubbles burst upon reaching the surface. Therefore, selecting mixing equipment with high mixing efficiency and solubility is particularly important.
Common mixing methods include aeration, mechanical mixing, jet mixing, and static mixing. Each of these methods has its own unique characteristics, yet all share the aforementioned drawbacks. Moreover, some methods are complicated to install or suffer from high equipment costs. Our company has spent many years researching and developing solutions to address this issue and has successfully achieved— Nano When this technology is applied to gas-mixing systems, the gas-mixing activator serves as a prime example of its implementation. It enables thorough emulsification of water and ozone gas. Since water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, its molecular structure is (H2O); however, in reality, water consists of numerous individual molecules tightly linked together to form large, complex aggregates. This device effectively separates these massive aggregates into smaller molecular structures, thereby activating the water and meeting the desired application requirements. High-concentration ozone, when dissolved in single-molecule water, exhibits exceptionally strong oxidizing power, making it highly effective at killing various microorganisms present in water. Its practical applications in mineral water plants and the food industry have yielded remarkable results.
-
- Recommended Solutions for Drinking Water Disinfection in Small Towns and Villages
-
Given the layout and characteristics of small towns and villages, it is more suitable to adopt a small-scale water intake and usage approach. For their disinfection treatment equipment, an integrated ozone generator/air-mixing disinfection system—with an overall structural design that ensures high reliability and relatively low cost—is required.
DJQ- Series Gas-Fluid Activator/Ozone Water Treatment Process
- Process Flow Diagram:
-
A complete ozone-activated water treatment system consists of several components, including: a water source, pre-filtration treatment, a DJQ-series ozone generator, a DJQ-series oxygen-mixing and activation device, a water purification tower, and a circulating pipeline.
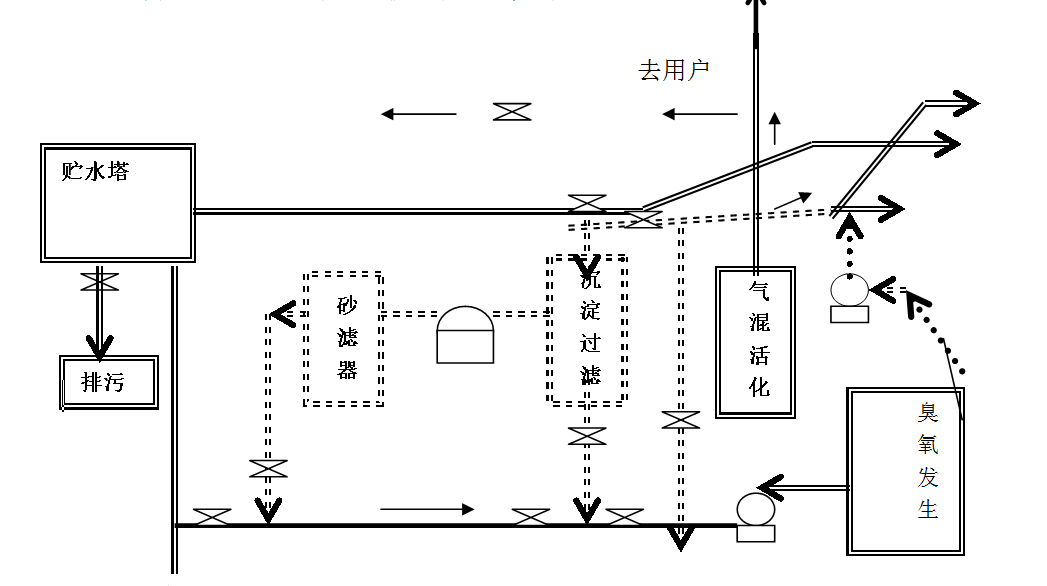
-
Depending on the varying water quality in different regions, actual water consumption levels, site-specific environmental conditions, and available funding, different treatment processes can be adopted.
- Process 1: Water pumped from the well—passed through a sedimentation and filtration basin—pumped again—through sand and chlorine (or activated carbon)—into a tank for further purification—pumped again—through the DJ-Q electrolytic ozone generator (oxygen-mixing activator)—and then flows into the water storage tower—ready for user consumption.
-
- Process 2: Water pumped from the well—passed through a sedimentation and filtration basin—pumped by a water pump—through a DJ-Q electrolytic ozone generator (oxygen-mixing activator)—and then enters the storage tank—finally reaching the user.
-
- Process 3: Water pumped from the well—DJ-Q electrolytic ozone generator—oxygen-mixing activator—into the water storage tank—user.
-
Under normal circumstances, the ozone generator—oxygen-activation unit continuously performs internal circulation treatment with the water in the storage tank. Depending on the degree of water contamination, the system typically needs to be operated only 3–4 times per day, each time for 1–1.5 hours. (On rainy or cloudy days, as well as in conditions of low atmospheric pressure and warm temperatures, the operating time should be appropriately extended.)
Ozone Generator - Oxygen-Mixing Activator/Ozone System: Functions and Applications
The efficacy of the ozone generator-oxygen mixing and activation system for water treatment.
- It can remove toxic and harmful substances from water, kill bacteria and algae, and oxidize certain heavy metal ions and organic compounds.
- After treatment, harmful substances such as nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfide in the water are significantly reduced.
- The system generates a large number of active free radicals in the water, which can rapidly eliminate various pathogenic bacterial strains.
- The electrode potential in the water treated by the system has significantly increased, indicating a substantial rise in dissolved oxygen levels and the formation of oxygen-rich water.
-
The Five Major Functions and Nine Key Benefits of Ozone Generators—Oxygen-Enrichment Activators
5 Great effect
9 Great effect
Active effect
Freshness retention effect; substance preservation effect
Purification effect
Antibacterial and sterilizing effect; self-cleaning ability effect; deodorizing and bleaching effect
Adjusting effect
Anti-oxidation effect; water softening effect
Reduction
Anti-rust effect
Precipitation effect
Flocculation and sedimentation effect
The ozone generator-oxygen activation device can be widely used in a variety of applications, including aquaculture, beverage processing plants, food production facilities, hotels and restaurants, swimming pools, public bathhouses, laundry and dyeing industries, industrial boilers, industrial cooling water systems, and water purification for rivers, lakes, and seas—as well as in the treatment of reclaimed water and wastewater.
Ozone Generator – Oxygen-Mixing Activator/Ozone System: Working Principle and Process Characteristics
- Working Principle: The ozone activation treatment process is an extremely important unit in drinking water treatment. Its basic principle is as follows: High-concentration ozone and oxygen generated by an ozone generator that electrolyzes pure water are introduced into a high-pressure water stream via a mixing and activation device. Under the effect of negative pressure, a large number of fine ozone bubbles are drawn into the water stream. These bubbles collide with, clash against, and even explode within the water, generating a series of energetic phenomena. This process produces far-infrared radiation at specific wavelengths and free electrons. Through electrochemical energy conversion, these phenomena ultimately result in the transformation of (H 2 0) and dissolved oxygen (O2) form oxygen ions (O²⁻). 2 ) and hydrogen peroxide (H 202 ). As a result, its affinity for other molecules in water is rapidly enhanced, enabling the generation of fine bubbles approximately 10 μm in size, thereby producing highly emulsified water with a high ozone concentration. The oxygen-mixing activator ensures thorough emulsification between water and ozone gas. Since water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, its molecular structure is (H 2 0), whereas in reality, water consists of numerous individual molecules that bond together to form massive complex structures. This device utilizes the DJQ-series generators—produced via nanotechnology—to separate these large complex structures into smaller molecular units, thereby activating them and meeting the desired application requirements. High-concentration ozone, when present in single-molecule water, exhibits extremely strong oxidizing power and possesses potent antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms in water.
-
Ozone in water is constantly undergoing reduction reactions, producing highly oxidizing singlet oxygen (O) and hydroxyl radicals.
Hydroxyl radicals (OH) can instantly decompose organic substances, bacteria, and microorganisms in water while also exhibiting excellent killing effects on various pathogenic microorganisms. Ozone's bactericidal speed is 600 to 3,000 times faster than chlorine; under the same sterilization conditions, it achieves a 99.9% kill rate for bacterial populations. Ozone can degrade sulfides, ammonia, and hydrides in water. After reacting with ozone, toxic sulfides, ammonia, and hydrides are transformed into non-toxic and harmless substances, thereby achieving the purpose of water purification.
The DJ-Q series oxygen-mixing activator/ozone drinking water treatment system produced by our company is extremely easy to install and compatible with existing water systems in small and medium-sized towns and villages. All you need to do is connect the inlet and outlet pipes of the water source to the DJ-Q series oxygen-mixing activator/ozone system, plug it into the power supply, and then, depending on the actual water quality requirements, activate one or more ozone generator units to adjust the ozone production. The installation, commissioning, and operation are simple and straightforward. This equipment boasts exceptionally high reliability—operating continuously for over 15,000 hours without any failures—and is remarkably easy to maintain. Should a fault occur, only the affected unit needs to be repaired or replaced, without disrupting normal operation.
- Water treated by this system has a high ozone solubility, and the residual ozone concentration in the water can reach 0.3–0.5 mg/L, effectively killing bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms in the water and degrading sulfides, ammonia, hydrides, and other substances, thereby achieving the purpose of water purification.
- Due to the high ozone concentration generated, using this method with the same amount of ozone introduced into water can achieve a higher ozone concentration in the water.
- When the system equipment is operating, it only requires a water pressure of 0.3 MPa or higher to function normally, thus saving energy.
- Produces fine 10-um bubbles with a long retention time, appearing white in color. It provides excellent emulsification and mixing, and delivers remarkable oxygenation and disinfection effects.
- No chemicals need to be added—safe and environmentally friendly.
- No recoil or replacement required, no failures and no maintenance needed—just inspect every 2–3 years. Low operating costs.
- The equipment features an integrated structure, is simple to install and debug, boasts stable and reliable performance, and can be flexibly moved and used. This equipment can produce: activated water with low viscosity and single-molecule structure; ozonated water with high ozone concentration; and oxygen-rich water with purification capabilities. As a result, it is suitable for treating various types of water bodies. Therefore, adopting this treatment process represents the most economical and effective method for addressing drinking water purification and disinfection challenges.
Keywords:
More news
Gather in Shanghai to attend the annual Fishery Expo.
Case Study: Highly Effective Sterilization Solutions for Food Factories
Nationwide sales hotline available 24/7
Address: Building 12, No. 168 Kechang Street, Qiubin Subdistrict, Wucheng District, Jinhua City, Zhejiang Province
E-mail:
Tel:
在线客服添加返回顶部
右侧在线客服样式 1,2,3 1
图片alt标题设置: Guangyuan Environmental
表单验证提示文本: Content cannot be empty!
循环体没有内容时: Sorry,no matching items were found.
CSS / JS 文件放置地


